F2FS: Hiểu về triển khai hệ thống tập tin qua mã nguồn mkfs.f2fs (Phần 2)
Phân tích mã nguồn mkfs.f2fs để hiểu bố cục đĩa cứng F2FS, khởi tạo SIT/NAT và quá trình tạo filesystem.
1. Lời nói đầu
Bài viết trước đã tóm tắt F2FS thông qua việc đọc paper, bài viết này sẽ đi sâu hơn để hiểu F2FS thông qua phân tích mã nguồn. Một mặt chúng ta có thể tìm hiểu F2FS thông qua các commit đầu tiên, mặt khác cũng có thể thông qua công cụ mkfs.f2fs của từng giai đoạn để hiểu trạng thái khởi tạo của một hệ thống tập tin. Mặc dù tính ổn định của những đoạn code này so với hiện tại chắc chắn là không đủ, nhưng như vậy vẫn sẽ dễ hiểu hơn các tính năng được đề cập trong paper.
Bài viết này trước tiên sẽ tìm hiểu bố cục đĩa cứng của F2FS đã được format (tức trạng thái khởi tạo của nó), chúng ta sẽ triển khai chi tiết thông qua debug mã nguồn công cụ mkfs.f2fs ngoài kernel.
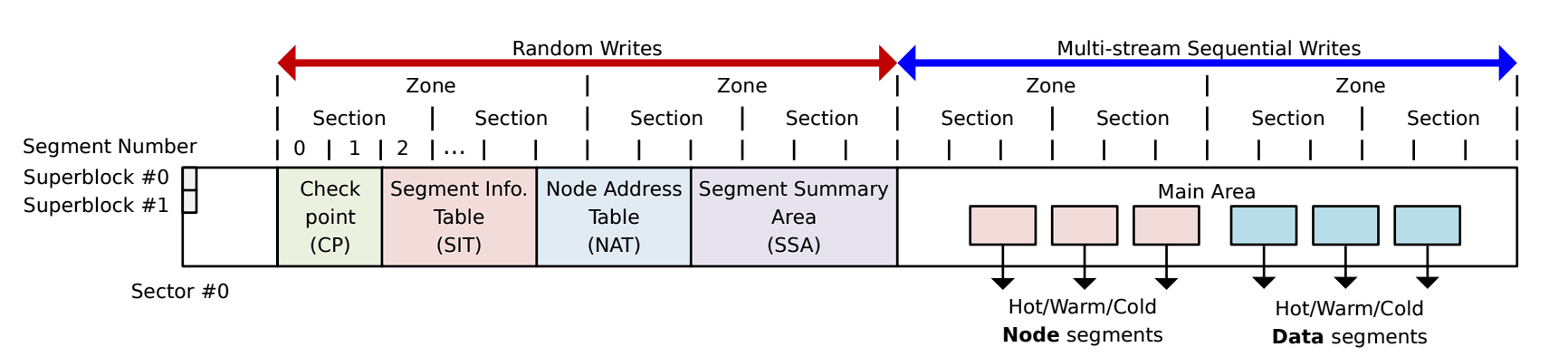
2. Tổng quan: Bố cục đĩa cứng
Như đã đề cập ở bài trước, bố cục của F2FS được chia thành 6 area như hình trên. Vậy trạng thái khởi tạo của nó như thế nào? Ở đây có thể thông qua debug mkfs.f2fs để hiểu các cấu trúc dữ liệu cụ thể.
Chuẩn bị trước khi bắt tay vào làm:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
git clone https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/jaegeuk/f2fs-tools.git
cd f2fs-tools
# Tìm commit gần với thời điểm code kernel ở trên, checkout qua đó
git checkout -b jintianxiaomidaobilema 036d45e551ca5405c726f8ccb51f446620cd4af4
cd mkfs
# Tạo một img 1GB để debug
dd if=/dev/zero of=f2fs.img bs=1024 count=1000000
# Compile mkfs.f2fs, sử dụng -g3 để thuận tiện cho việc debug macro expansion
gcc f2fs_format.c -g3 -o mkfs.f2fs
Cấu trúc dữ liệu F2FS “trên giấy” có thể xem trực tiếp tại đây, tác giả comment rất chi tiết.
Trước tiên đặt breakpoint trước khi return trong quy trình chính khởi tạo f2fs_format_device(), sau đó truyền tham số khởi động và output biến f2fs_params. Biến này được sử dụng để parse options trước khi khởi tạo, chúng ta cũng có thể thấy hành vi mặc định của nó như thế nào:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
(gdb) b f2fs_format.c:1273
(gdb) r f2fs.img
(gdb) set print pretty on
(gdb) p f2fs_params
$1 = {
sector_size = 512,
reserved_segments = 25,
overprovision = 5,
cur_seg = {473, 1, 0, 476, 475, 474},
segs_per_sec = 1,
secs_per_zone = 1,
start_sector = 0,
total_sectors = 2000000,
sectors_per_blk = 8,
blks_per_seg = 512,
vol_label = "F2FS", '\000' <repeats 11 times>,
heap = 1,
fd = 3,
device_name = 0x7fffffffe137 "f2fs.img",
extension_list = 0x0
}
Một số thông tin như sau:
- overprovision là phần trăm không gian dự trữ cho GC, không mở cho người dùng sử dụng. reserved_segments được tính toán từ overprovision
- Mặc định sử dụng heap-based allocation (
heap = 1), thực ra là ảnh hưởng đến hành vi gán giá trị củacur_seg. Như đã đề cập bên dưới, data bắt đầu từ địa chỉ đầu, còn node thì bắt đầu từ địa chỉ cuối fdchỉ được sử dụng chowritetodisk()để cuối cùng ghi vào thiết bị/file ảnh, không thực sự lưu trữ trong hệ thống tập tin
3. Khởi tạo Super block
Cấu trúc dữ liệu trong f2fs.h như sau:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
/* * For superblock */
struct f2fs_super_block {
__le32 magic; /* Magic Number */
__le16 major_ver; /* Major Version */
__le16 minor_ver; /* Minor Version */
__le32 log_sectorsize; /* log2 sector size in bytes */
__le32 log_sectors_per_block; /* log2 # of sectors per block */
__le32 log_blocksize; /* log2 block size in bytes */
__le32 log_blocks_per_seg; /* log2 # of blocks per segment */
__le32 segs_per_sec; /* # of segments per section */
__le32 secs_per_zone; /* # of sections per zone */
__le32 checksum_offset; /* checksum offset inside super block */
__le64 block_count; /* total # of user blocks */
__le32 section_count; /* total # of sections */
__le32 segment_count; /* total # of segments */
__le32 segment_count_ckpt; /* # of segments for checkpoint */
__le32 segment_count_sit; /* # of segments for SIT */
__le32 segment_count_nat; /* # of segments for NAT */
__le32 segment_count_ssa; /* # of segments for SSA */
__le32 segment_count_main; /* # of segments for main area */
__le32 segment0_blkaddr; /* start block address of segment 0 */
__le32 cp_blkaddr; /* start block address of checkpoint */
__le32 sit_blkaddr; /* start block address of SIT */
__le32 nat_blkaddr; /* start block address of NAT */
__le32 ssa_blkaddr; /* start block address of SSA */
__le32 main_blkaddr; /* start block address of main area */
__le32 root_ino; /* root inode number */
__le32 node_ino; /* node inode number */
__le32 meta_ino; /* meta inode number */
__u8 uuid[16]; /* 128-bit uuid for volume */
__le16 volume_name[512]; /* volume name */
__le32 extension_count; /* # of extensions below */
__u8 extension_list[F2FS_MAX_EXTENSION][8]; /* extension array */
} __packed;
Tương tự sử dụng gdb để dump trạng thái khởi tạo, như sau:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
(gdb) p super_block
$2 = {
magic = 4076150800,
major_ver = 1,
minor_ver = 0,
log_sectorsize = 9,
log_sectors_per_block = 3,
log_blocksize = 12,
log_blocks_per_seg = 9,
segs_per_sec = 1,
secs_per_zone = 1,
checksum_offset = 0,
block_count = 250000,
section_count = 478,
segment_count = 487,
segment_count_ckpt = 2,
segment_count_sit = 2,
segment_count_nat = 4,
segment_count_ssa = 1,
segment_count_main = 478,
failure_safe_block_distance = 0,
segment0_blkaddr = 512,
start_segment_checkpoint = 512,
sit_blkaddr = 1536,
nat_blkaddr = 2560,
ssa_blkaddr = 4608,
main_blkaddr = 5120,
root_ino = 3,
node_ino = 1,
meta_ino = 2,
volume_serial_number = 0,
volume_name = {70, 50, 70, 83, 0 <repeats 508 times>},
extension_count = 22,
extension_list = {"jpg\000\000\000\000", "gif\000\000\000\000", "png\000\000\000\000", "avi\000\000\000\000", "divx\000\000\000", "mp4\000\000\000\000", "mp3\000\000\000\000",
"3gp\000\000\000\000", "wmv\000\000\000\000", "wma\000\000\000\000", "mpeg\000\000\000", "mkv\000\000\000\000", "mov\000\000\000\000", "asx\000\000\000\000", "asf\000\000\000\000",
"wmx\000\000\000\000", "svi\000\000\000\000", "wvx\000\000\000\000", "wm\000\000\000\000\000", "mpg\000\000\000\000", "mpe\000\000\000\000", "rm\000\000\000\000\000",
"ogg\000\000\000\000", "\000\000\000\000\000\000\000" <repeats 41 times>}
}
Phần super block khá dễ hiểu, ngoài việc cấu hình thông tin cơ bản về block device block/sector cũng như số lượng segment, còn phản ánh phân chia ba cấp segment-section-zone 1:1:1 mặc định, cũng như địa chỉ bắt đầu của các area (*_blkaddr).
4. Khởi tạo SIT
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
/**
* @brief It initialize SIT Data structure
* @param None
* @return 0 if success
*/
static int8_t f2fs_init_sit_area(void)
{
u_int32_t blk_size_bytes;
u_int32_t seg_size_bytes;
u_int32_t index = 0;
u_int64_t sit_seg_blk_offset = 0;
u_int8_t *zero_buf = NULL;
blk_size_bytes = 1 << le32_to_cpu(super_block.log_blocksize);
seg_size_bytes = (1 << le32_to_cpu(super_block.log_blocks_per_seg)) *
blk_size_bytes;
zero_buf = calloc(sizeof(u_int8_t), seg_size_bytes);
if(zero_buf == NULL) {
printf("\n\tError: Calloc Failed for sit_zero_buf!!!\n");
return -1;
}
sit_seg_blk_offset = le32_to_cpu(super_block.sit_blkaddr) *
blk_size_bytes;
for (index = 0;
index < (le32_to_cpu(super_block.segment_count_sit) / 2);
index++) {
if (writetodisk(f2fs_params.fd, zero_buf, sit_seg_blk_offset,
seg_size_bytes) < 0) {
printf("\n\tError: While zeroing out the sit area \
on disk!!!\n");
return -1;
}
sit_seg_blk_offset = sit_seg_blk_offset + seg_size_bytes;
}
free(zero_buf);
return 0 ;
}
/**
* @brief Ghi buffer vào đĩa hoặc thiết bị lưu trữ cần được format
* với F2FS.
* @param fd File descriptor cho thiết bị
* @param buf buffer cần ghi
* @param offset vị trí ghi trên thiết bị
* @param length độ dài của thiết bị
* @return 0 nếu thành công
*/
static int writetodisk(int32_t fd, void *buf, u_int64_t offset, size_t length)
{
if (lseek64(fd, offset, SEEK_SET) < 0) {
printf("\n\tError: While lseek to the derised location!!!\n");
return -1;
}
if (write(fd, buf, length) < 0) {
printf("\n\tError: While writing data to the disk!!! Error Num : \
%d\n", errno);
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
Trong hàm khởi tạo SIT f2fs_init_sit_area(), không có thay đổi gì trên cấu trúc dữ liệu trong bộ nhớ, cốt lõi chỉ là writetodisk() ghi vào cấu trúc dữ liệu ngoại vi tương ứng với SIT.
Từ dump trước đó có thể thấy super_block.segment_count_sit = 2, tức SIT area thực tế sử dụng 2 segment, nhưng ở đây chỉ ghi một nửa (1 segment) vào ngoại vi image, nội dung được ghi đều là số 0 (zero_buf).
5. Khởi tạo NAT
Hiện tại hành vi khởi tạo NAT giống với SIT, khác biệt là NAT chiếm 4 segment, các segment khác tương tự.
Lưu ý: Trong giai đoạn khởi tạo root directory sau này, NAT vẫn cần thực hiện thêm các thao tác cập nhật cho root inode.
6. Khởi tạo Root directory
Quy trình tiếp theo thực thi f2fs_create_root_dir(), đơn giản có 3 bước:
f2fs_write_root_inode(): Tạo root inode trong main areaf2fs_update_nat_root(): Tiếp tục khởi tạo NAT, tức ghi lại address mapping của root inode trong area nàyf2fs_add_default_dentry_root()
Chúng ta sẽ xem đoạn code dài này:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
/**
* @brief Khởi tạo và ghi root inode lên thiết bị.
* @param None
* @return 0 nếu thành công
*/
static int8_t f2fs_write_root_inode(void)
{
struct f2fs_node *raw_node = NULL;
u_int32_t blk_size_bytes;
u_int64_t data_blk_nor;
u_int64_t main_area_node_seg_blk_offset = 0;
raw_node = calloc(sizeof(struct f2fs_node), 1);
if (raw_node == NULL) {
printf("\n\tError: Calloc Failed for raw_node!!!\n");
return -1;
}
// Thiết lập root inode number
raw_node->footer.nid = super_block.root_ino;
raw_node->footer.ino = super_block.root_ino;
raw_node->footer.cp_ver = cpu_to_le64(1);
// Trỏ đến block tiếp theo
raw_node->footer.next_blkaddr = cpu_to_le32(
le32_to_cpu(super_block.main_blkaddr) +
f2fs_params.cur_seg[CURSEG_HOT_NODE] *
f2fs_params.blks_per_seg + 1);
raw_node->i.i_mode = cpu_to_le16(0x41ed);
raw_node->i.i_links = cpu_to_le32(2);
raw_node->i.i_uid = cpu_to_le32(getuid());
raw_node->i.i_gid = cpu_to_le32(getgid());
blk_size_bytes = 1 << le32_to_cpu(super_block.log_blocksize);
// Kích thước file theo các đơn vị khác nhau (byte/block)
raw_node->i.i_size = cpu_to_le64(1 * blk_size_bytes); /* dentry */
raw_node->i.i_blocks = cpu_to_le64(2);
raw_node->i.i_ctime = cpu_to_le32(time(NULL));
raw_node->i.i_ctime_nsec = 0;
raw_node->i.i_mtime = cpu_to_le32(time(NULL));
raw_node->i.i_mtime_nsec = 0;
raw_node->i.i_xattr_nid = 0;
raw_node->i.i_flags = 0;
raw_node->i.current_depth = cpu_to_le32(1);
// Vị trí của HOT DATA
data_blk_nor = le32_to_cpu(super_block.main_blkaddr) +
f2fs_params.cur_seg[CURSEG_HOT_DATA] * f2fs_params.blks_per_seg;
// i_addr[ADDRS_PER_INODE=927] là con trỏ trỏ đến data block
raw_node->i.i_addr[0] = cpu_to_le32(data_blk_nor);
raw_node->i.i_ext.fofs = 0;
raw_node->i.i_ext.blk_addr = cpu_to_le32(data_blk_nor);
raw_node->i.i_ext.len = cpu_to_le32(1);
// Trước tiên lấy địa chỉ bắt đầu của main area
main_area_node_seg_blk_offset = le32_to_cpu(super_block.main_blkaddr);
// Vị trí của HOT NODE
main_area_node_seg_blk_offset += f2fs_params.cur_seg[CURSEG_HOT_NODE] *
f2fs_params.blks_per_seg;
main_area_node_seg_blk_offset *= blk_size_bytes;
// Ghi root inode vào HOT NODE offset
if (writetodisk(f2fs_params.fd, raw_node, main_area_node_seg_blk_offset,
sizeof(struct f2fs_node)) < 0) {
printf("\n\tError: While writing the raw_node to disk!!!\n");
return -1;
}
memset(raw_node, 0xff, sizeof(struct f2fs_node));
// Block tiếp theo bắt đầu điền toàn bộ 0xff
if (writetodisk(f2fs_params.fd, raw_node,
main_area_node_seg_blk_offset + 4096,
sizeof(struct f2fs_node)) < 0) {
printf("\n\tError: While writing the raw_node to disk!!!\n");
return -1;
}
free(raw_node);
return 0;
}
/**
* @brief Cập nhật NAT cho Root Inode
* @param None
* @return 0 nếu thành công
*/
static int8_t f2fs_update_nat_root(void)
{
// Cấu trúc dữ liệu có kích thước một block, chứa 4k/sizeof(f2fs_nat_entry)
// entry f2fs_nat_entry
// Entry này là một bộ ba <version, ino, block_addr>, ý nghĩa dễ hiểu,
// chính là mapping entry từ ino đến addr
struct f2fs_nat_block *nat_blk = NULL;
u_int32_t blk_size_bytes;
u_int64_t nat_seg_blk_offset = 0;
nat_blk = calloc(sizeof(struct f2fs_nat_block), 1);
if(nat_blk == NULL) {
printf("\n\tError: Calloc Failed for nat_blk!!!\n");
return -1;
}
/* update root */
// Thực hiện mapping từ ino đến addr của root inode,
// phân tích trước đã biết địa chỉ
nat_blk->entries[super_block.root_ino].block_addr = cpu_to_le32(
le32_to_cpu(super_block.main_blkaddr) +
f2fs_params.cur_seg[CURSEG_HOT_NODE] * f2fs_params.blks_per_seg);
nat_blk->entries[super_block.root_ino].ino = super_block.root_ino;
// Còn lại là node inode (ino=1) và meta inode (ino=2)
/* update node nat */
// Không hiểu tại sao là 1
nat_blk->entries[super_block.node_ino].block_addr = cpu_to_le32(1);
nat_blk->entries[super_block.node_ino].ino = super_block.node_ino;
/* update meta nat */
nat_blk->entries[super_block.meta_ino].block_addr = cpu_to_le32(1);
nat_blk->entries[super_block.meta_ino].ino = super_block.meta_ino;
blk_size_bytes = 1 << le32_to_cpu(super_block.log_blocksize);
// Định vị rồi ghi vào vị trí NAT
nat_seg_blk_offset = le32_to_cpu(super_block.nat_blkaddr) *
blk_size_bytes;
if (writetodisk(f2fs_params.fd, nat_blk, nat_seg_blk_offset,
sizeof(struct f2fs_nat_block)) < 0) {
printf("\n\tError: While writing the nat_blk set0 to disk!!!\n");
return -1;
}
free(nat_blk);
return 0;
}
/**
* @brief Cập nhật default dentries trong Root Inode
* @param None
* @return 0 nếu thành công
*/
static int8_t f2fs_add_default_dentry_root(void)
{
// Bổ sung background về dentry block:
// đại khái bao gồm một bitmap table và nhiều dentry, xem bonus chi tiết bên dưới
struct f2fs_dentry_block *dent_blk = NULL;
u_int32_t blk_size_bytes;
u_int64_t data_blk_offset = 0;
dent_blk = calloc(sizeof(struct f2fs_dentry_block), 1);
if(dent_blk == NULL) {
printf("\n\tError: Calloc Failed for dent_blk!!!\n");
return -1;
}
// Điền thông tin dentry liên quan đến root inode (. và ..)
dent_blk->dentry[0].hash_code = 0;
dent_blk->dentry[0].ino = super_block.root_ino;
dent_blk->dentry[0].name_len = cpu_to_le16(1);
dent_blk->dentry[0].file_type = F2FS_FT_DIR;
memcpy(dent_blk->filename[0], ".", 1);
dent_blk->dentry[1].hash_code = 0;
dent_blk->dentry[1].ino = super_block.root_ino;
dent_blk->dentry[1].name_len = cpu_to_le16(2);
dent_blk->dentry[1].file_type = F2FS_FT_DIR;
memcpy(dent_blk->filename[1], "..", 2);
/* bitmap for . and .. */
// Viết tay bitmap, bit 0 và 1 đã tồn tại
dent_blk->dentry_bitmap[0] = (1 << 1) | (1 << 0);
blk_size_bytes = 1 << le32_to_cpu(super_block.log_blocksize);
data_blk_offset = (le32_to_cpu(super_block.main_blkaddr) +
f2fs_params.cur_seg[CURSEG_HOT_DATA] *
f2fs_params.blks_per_seg) * blk_size_bytes;
// Ghi vào HOT DATA
if (writetodisk(f2fs_params.fd, dent_blk, data_blk_offset,
sizeof(struct f2fs_dentry_block)) < 0) {
printf("\n\tError: While writing the dentry_blk to disk!!!\n");
return -1;
}
free(dent_blk);
return 0;
}
f2fs_write_root_inode() xử lý tương tự như inode ở tầng VFS. Một số xử lý đặc biệt của F2FS bao gồm:
- root inode được ghi vào HOT NODE, tức vị trí bắt đầu của NODE
i_addr[0]của root inode làm con trỏ trỏ đến data, trỏ đến HOT DATA
Thông tin output liên quan đến root inode như sau (lưu ý
ivàdn/inlà mộtunion, output của hai cái sau hiện tại không có ý nghĩa):
f2fs_update_nat_root() tiếp tục quá trình khởi tạo NAT như trước đó, NAT vẫn cần thực hiện xử lý mapping cho root inode, cụ thể là sử dụng một block đại diện cho nhiều mapping entry, sau đó ghi lại giá trị mapping từ inode đến addr, cuối cùng ghi vào NAT area.
f2fs_add_default_dentry_root() là bổ sung thông tin dentry cần thiết cho root inode, xử lý . và .., điền bitmap và ghi vào HOT DATA.
Bonus: Một số thông tin về
dentry
Thuộc tính của
dentrykhá trực quan, định vị file không gì khác ngoài thông tin file type và hash này.Một dentry block bao gồm:
- bitmap để truy vấn và cập nhật nhanh
- reserved u8bits có lẽ không dùng đến
dentryarray để định vị file- filename string pool để ghi tên
Chúng ta xem sâu hơn về layout cụ thể của dentry block:
Tức là trong một dentry block:
- Lưu trữ 214 dentry, chiếm $214 \times 11 = 2354 \text{ bytes}$
- Phần string chiếm $214 \times 8 = 1712 \text{ bytes}$
- bitmap làm tròn lên được $\lceil \frac{214}{8} \rceil = 27 \text{ bytes}$
- Phần còn lại theo một block 4k trừ đi là $4096 - 2354 - 1712 - 27 = 3 \text{ bytes}$
Do đó chọn giá trị 214 là để tối đa hóa tỷ lệ sử dụng dentry block ($\text{reserved} < 19(+1\text{bit}) \text{ bytes}$).
7. Khởi tạo Check point
7.1. Quy trình
Phần khởi tạo check point cũng là một quy trình dài, phần này không chỉ liên quan đến check point mà còn có cấu trúc dữ liệu summary block:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
/**
* @brief Ghi check point pack vào Check point Area
* @param None
* @return 0 nếu thành công
*/
static int8_t f2fs_write_check_point_pack(void)
{
struct f2fs_checkpoint *ckp = NULL;
struct f2fs_summary_block *sum = NULL;
u_int32_t blk_size_bytes;
u_int64_t cp_seg_blk_offset = 0;
u_int32_t crc = 0;
int i;
ckp = calloc(F2FS_CP_BLOCK_SIZE, 1);
if (ckp == NULL) {
printf("\n\tError: Calloc Failed for f2fs_checkpoint!!!\n");
return -1;
}
sum = calloc(sizeof(struct f2fs_summary_block), 1);
if (sum == NULL) {
printf("\n\tError: Calloc Failed for summay_node!!!\n");
return -1;
}
// Mỗi check point chia thành 2 page (block) để tạo thành, đặt ở đầu và cuối,
// khi recovery nếu giống nhau thì biểu thị hợp lệ
// Đồng thời CP area tồn tại 2 phiên bản check point khác nhau (check point pack),
// cập nhật luân phiên
/* 1. cp page 1 of checkpoint pack 1 */
// version hiện tại đặt là 1
ckp->checkpoint_ver = 1;
// Ghi lại segment number bắt đầu hiện tại của các log,
// chúng ta đã đưa ra giá trị cụ thể ở trước
ckp->cur_node_segno[0] =
cpu_to_le32(f2fs_params.cur_seg[CURSEG_HOT_NODE]);
ckp->cur_node_segno[1] =
cpu_to_le32(f2fs_params.cur_seg[CURSEG_WARM_NODE]);
ckp->cur_node_segno[2] =
cpu_to_le32(f2fs_params.cur_seg[CURSEG_COLD_NODE]);
ckp->cur_data_segno[0] =
cpu_to_le32(f2fs_params.cur_seg[CURSEG_HOT_DATA]);
ckp->cur_data_segno[1] =
cpu_to_le32(f2fs_params.cur_seg[CURSEG_WARM_DATA]);
ckp->cur_data_segno[2] =
cpu_to_le32(f2fs_params.cur_seg[CURSEG_COLD_DATA]);
// Tác giả nói lý thuyết cung cấp 16 log, nhưng mặc định chỉ dùng 6 cái
// (node/data mỗi loại 3 cái), những cái không dùng thì điền 0xff
for (i = 3; i < MAX_ACTIVE_NODE_LOGS; i++) {
ckp->cur_node_segno[i] = 0xffffffff;
ckp->cur_data_segno[i] = 0xffffffff;
}
ckp->cur_node_blkoff[0] = cpu_to_le16(1);
ckp->nat_upd_blkoff[0] = cpu_to_le16(1);
ckp->cur_data_blkoff[0] = cpu_to_le16(1);
// Có lẽ chỉ có HOT DATA và HOT NODE mỗi cái chiếm một block,
// xem phần khởi tạo NAT trước đó
ckp->valid_block_count = cpu_to_le64(2);
ckp->rsvd_segment_count = cpu_to_le32(f2fs_params.reserved_segments);
// Những tính toán phức tạp này xem dump sau
ckp->overprov_segment_count = cpu_to_le32(
(le32_to_cpu(super_block.segment_count_main) -
le32_to_cpu(ckp->rsvd_segment_count)) *
f2fs_params.overprovision / 100);
ckp->overprov_segment_count = cpu_to_le32(
le32_to_cpu(ckp->overprov_segment_count) +
le32_to_cpu(ckp->rsvd_segment_count));
/* main segments - reserved segments - (node + data segments) */
// Ở đây free_segment_count chỉ số lượng free segment trong main area
// Không hiểu tại sao lại hardcode là 6... có lẽ 6 log mỗi cái chiếm 1 segment?
ckp->free_segment_count = cpu_to_le32(
le32_to_cpu(super_block.segment_count_main) - 6);
// Trừ đi phần overprov dự trữ
ckp->user_block_count = cpu_to_le64(
((le32_to_cpu(ckp->free_segment_count) + 6 -
le32_to_cpu(ckp->overprov_segment_count)) *
f2fs_params.blks_per_seg));
// checkpoint tổng cộng dùng 5 block
ckp->cp_pack_total_block_count = cpu_to_le32(5);
ckp->cp_pack_start_sum = cpu_to_le32(1);
ckp->valid_node_count = cpu_to_le32(1);
ckp->valid_inode_count = cpu_to_le32(1);
ckp->next_free_nid = cpu_to_le32(
le32_to_cpu(super_block.root_ino) + 1);
// Trước đó thấy chỉ ghi một nửa SIT, do đó là /2, NAT sau đó tương tự
ckp->sit_ver_bitmap_bytesize = cpu_to_le32(
((le32_to_cpu(super_block.segment_count_sit) / 2) <<
le32_to_cpu(super_block.log_blocks_per_seg)) / 8);
ckp->nat_ver_bitmap_bytesize = cpu_to_le32(
((le32_to_cpu(super_block.segment_count_nat) / 2) <<
le32_to_cpu(super_block.log_blocks_per_seg)) / 8);
ckp->checksum_offset = cpu_to_le32(4092);
crc = f2fs_cal_crc32(F2FS_SUPER_MAGIC, ckp,
le32_to_cpu(ckp->checksum_offset));
*((u_int32_t *)((unsigned char *)ckp +
le32_to_cpu(ckp->checksum_offset))) = crc;
blk_size_bytes = 1 << le32_to_cpu(super_block.log_blocksize);
// Hiện tại đang ở địa chỉ bắt đầu của check point area
cp_seg_blk_offset =
le32_to_cpu(super_block.start_segment_checkpoint) * blk_size_bytes;
// Ghi phần này vào ngoại vi
if (writetodisk(f2fs_params.fd, ckp, cp_seg_blk_offset,
F2FS_CP_BLOCK_SIZE) < 0) {
printf("\n\tError: While writing the ckp to disk!!!\n");
return -1;
}
/* 2. Chuẩn bị và ghi Segment summary cho data blocks */
// Từ đây bắt đầu liên quan đến cấu trúc dữ liệu summary,
// có thể xem phân tích summary ở phần dưới
SET_SUM_TYPE((&sum->footer), SUM_TYPE_DATA);
// summary đầu tiên trong entries là root inode
sum->entries[0].nid = super_block.root_ino;
sum->entries[0].bidx = 0;
// Block thứ hai điền summary
cp_seg_blk_offset += blk_size_bytes;
if (writetodisk(f2fs_params.fd, sum, cp_seg_blk_offset,
sizeof(struct f2fs_summary_block)) < 0) {
printf("\n\tError: While writing the sum_blk to disk!!!\n");
return -1;
}
/* 3. Điền segment summary cho data block bằng số 0 */
memset(sum, 0, sizeof(struct f2fs_summary_block));
cp_seg_blk_offset += blk_size_bytes;
// Block thứ ba điền số 0
if (writetodisk(f2fs_params.fd, sum, cp_seg_blk_offset,
sizeof(struct f2fs_summary_block)) < 0) {
printf("\n\tError: While writing the sum_blk to disk!!!\n");
return -1;
}
/* 4. Điền segment summary cho data block bằng số 0 */
memset(sum, 0, sizeof(struct f2fs_summary_block));
/* inode sit cho root */
// Ghi lại thông tin journal của SIT, chia thành node và data, mỗi loại 3 entry
sum->n_sits = cpu_to_le16(6);
sum->sit_j.entries[0].segno = ckp->cur_node_segno[0];
sum->sit_j.entries[0].se.vblocks = cpu_to_le16((CURSEG_HOT_NODE << 10) | 1);
f2fs_set_bit(0, sum->sit_j.entries[0].se.valid_map);
sum->sit_j.entries[1].segno = ckp->cur_node_segno[1];
sum->sit_j.entries[1].se.vblocks = cpu_to_le16((CURSEG_WARM_NODE << 10));
sum->sit_j.entries[2].segno = ckp->cur_node_segno[2];
sum->sit_j.entries[2].se.vblocks = cpu_to_le16((CURSEG_COLD_NODE << 10));
/* data sit cho root */
sum->sit_j.entries[3].segno = ckp->cur_data_segno[0];
sum->sit_j.entries[3].se.vblocks = cpu_to_le16((CURSEG_HOT_DATA << 10) | 1);
f2fs_set_bit(0, sum->sit_j.entries[3].se.valid_map);
sum->sit_j.entries[4].segno = ckp->cur_data_segno[1];
sum->sit_j.entries[4].se.vblocks = cpu_to_le16((CURSEG_WARM_DATA << 10));
sum->sit_j.entries[5].segno = ckp->cur_data_segno[2];
sum->sit_j.entries[5].se.vblocks = cpu_to_le16((CURSEG_COLD_DATA << 10));
cp_seg_blk_offset += blk_size_bytes;
// Block thứ tư điền SIT journal
if (writetodisk(f2fs_params.fd, sum, cp_seg_blk_offset,
sizeof(struct f2fs_summary_block)) < 0) {
printf("\n\tError: While writing the sum_blk to disk!!!\n");
return -1;
}
/* 5. cp page2 */
cp_seg_blk_offset += blk_size_bytes;
// Block thứ năm điền bản sao check point ở cuối
if (writetodisk(f2fs_params.fd, ckp, cp_seg_blk_offset,
F2FS_CP_BLOCK_SIZE) < 0) {
printf("\n\tError: While writing the ckp to disk!!!\n");
return -1;
}
/* 6. cp page 1 của check point pack 2
* Khởi tạo checkpoint pack khác với version zero
*/
// Ở đây checkpoint chỉ thay đổi version và CRC
ckp->checkpoint_ver = 0;
crc = f2fs_cal_crc32(F2FS_SUPER_MAGIC, ckp,
le32_to_cpu(ckp->checksum_offset));
*((u_int32_t *)((unsigned char *)ckp +
le32_to_cpu(ckp->checksum_offset))) = crc;
// Từ địa chỉ bắt đầu check point offset một section
// tức offset 512 block
cp_seg_blk_offset = (le32_to_cpu(super_block.start_segment_checkpoint) +
f2fs_params.blks_per_seg) *
blk_size_bytes;
// Block thứ 512 ghi check point#0
if (writetodisk(f2fs_params.fd, ckp,
cp_seg_blk_offset, F2FS_CP_BLOCK_SIZE) < 0) {
printf("\n\tError: While writing the ckp to disk!!!\n");
return -1;
}
/* 7. */
memset(sum, 0, sizeof(struct f2fs_summary_block));
SET_SUM_TYPE((&sum->footer), SUM_TYPE_DATA);
cp_seg_blk_offset += blk_size_bytes;
// Block thứ 512 + 1 ghi số 0
if (writetodisk(f2fs_params.fd, sum, cp_seg_blk_offset,
sizeof(struct f2fs_summary_block)) < 0) {
printf("\n\tError: While writing the sum_blk to disk!!!\n");
return -1;
}
/* 8. */
memset(sum, 0, sizeof(struct f2fs_summary_block));
cp_seg_blk_offset += blk_size_bytes;
// Block thứ 512 + 2 ghi số 0
if (writetodisk(f2fs_params.fd, sum, cp_seg_blk_offset,
sizeof(struct f2fs_summary_block)) < 0) {
printf("\n\tError: While writing the sum_blk to disk!!!\n");
return -1;
}
/* 9. */
memset(sum, 0, sizeof(struct f2fs_summary_block));
cp_seg_blk_offset += blk_size_bytes;
// Block thứ 512 + 3 ghi số 0
if (writetodisk(f2fs_params.fd, sum, cp_seg_blk_offset,
sizeof(struct f2fs_summary_block)) < 0) {
printf("\n\tError: While writing the sum_blk to disk!!!\n");
return -1;
}
/* 10. cp page 2 của check point pack 2 */
cp_seg_blk_offset += blk_size_bytes;
// Block thứ 512 + 4 ghi bản sao check point ở cuối
if (writetodisk(f2fs_params.fd, ckp, cp_seg_blk_offset,
F2FS_CP_BLOCK_SIZE) < 0) {
printf("\n\tError: While writing the ckp to disk!!!\n");
return -1;
}
free(sum);
free(ckp);
return 0;
}
7.2. Summary block
Summary block trong quy trình ban đầu nhìn khá khó hiểu, cần sắp xếp lại cấu trúc dữ liệu:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
////////////////// summary tổng thể
struct f2fs_summary_block {
// #define ENTRIES_IN_SUM 512
struct f2fs_summary entries[ENTRIES_IN_SUM];
union {
__le16 n_nats; // độ dài hợp lệ của nat_j.entries[] (độ dài thực tế cố định)
__le16 n_sits; // độ dài hợp lệ của sit_j.entries[] (độ dài thực tế cố định)
};
// Kích thước là 4k - sizeof(f2fs_summary)*512 - sizeof(summary_footer)
union {
struct nat_journal nat_j;
struct sit_journal sit_j;
};
struct summary_footer footer;
} __attribute__((packed));
// Ghi lại reverse mapping, tức node to parent
struct f2fs_summary {
__le32 nid; /* parent node id */
union {
__u8 reserved[3];
struct {
__u8 version; /* node version number */
__le16 bidx; /* block index in parent node */
} __attribute__((packed));
};
} __attribute__((packed));
////////////////// journal entry
// sizeof(struct nat_journal) = 505
// NAT_JOURNAL_ENTRIES = 38
struct nat_journal {
struct nat_journal_entry entries[NAT_JOURNAL_ENTRIES];
__u8 reserved[NAT_JOURNAL_RESERVED];
} __attribute__((packed));
// sizeof(struct sit_journal) = 505
// SIT_JOURNAL_ENTRIES = 6
struct sit_journal {
struct sit_journal_entry entries[SIT_JOURNAL_ENTRIES];
__u8 reserved[SIT_JOURNAL_RESERVED];
} __attribute__((packed));
////////////////// journal entry bên ngoài
struct nat_journal_entry {
__le32 nid;
struct f2fs_nat_entry ne;
} __attribute__((packed));
// sizeof(struct sit_journal_entry) = 505
struct sit_journal_entry {
__le32 segno;
struct f2fs_sit_entry se;
} __attribute__((packed));
////////////////// entry thực tế của hai loại area
// Trước đó cũng đã thấy qua bộ ba NAT
struct f2fs_nat_entry {
__u8 version;
__le32 ino;
__le32 block_addr;
} __attribute__((packed));
// Do SIT không có quy trình khởi tạo phức tạp nên trông xa lạ
struct f2fs_sit_entry {
__le16 vblocks; // ý nghĩa là valid blocks
__u8 valid_map[SIT_VBLOCK_MAP_SIZE];
__le64 mtime;
} __attribute__((packed));
////////////////// footer phụ trợ
// footer đặt ở cuối summary, dùng để phân biệt loại summary và checksum để kiểm tra tính nhất quán
struct summary_footer {
unsigned char entry_type;
__u32 check_sum;
} __attribute__((packed));
Mặc dù cấu trúc dữ liệu không chỉ nhiều mà còn trông phức tạp, nhưng không khó hiểu:
f2fs_summary_block: Mô tả nhiều summary entry được lưu trữ theo đơn vị block trên ngoại vi, không gian còn lại lưu journalf2fs_summary: Reverse mapping, ghi lại parent node tương ứng và block index trong parentnat_journal/sit_journal: Entry của journal, chứa nhiều journal entrynat_journal_entry/sit_journal_entry: Journal entry, bao gồm id và area entry cụ thểf2fs_nat_entry/f2fs_sit_entry: Entry thực tế cần check point ghi lại, tương ứng với cấu trúc dữ liệu của các area khác nhausummary_footer: Lưu ở cuối summary block, dùng để phân biệt loại journal và lưu checksum để kiểm tra
7.3. Thông tin debug hỗ trợ
Thông tin debug như sau, đặt breakpoint trước free():
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
(gdb) b f2fs_format.c:956
(gdb) info locals
ckp = 0x4098c0
sum = 0
blk_size_bytes = 4096
cp_seg_blk_offset = 4210688
crc = 1257347361
i = 8
(gdb) p *ckp
$6 = {
checkpoint_ver = 0,
user_block_count = 220672,
valid_block_count = 2,
rsvd_segment_count = 25,
overprov_segment_count = 47,
free_segment_count = 472,
cur_node_segno = {476, 475, 474, 4294967295, 4294967295, 4294967295, 4294967295, 4294967295},
cur_node_blkoff = {1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
nat_upd_blkoff = {1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
cur_data_segno = {473, 1, 0, 4294967295, 4294967295, 4294967295, 4294967295, 4294967295},
cur_data_blkoff = {1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
ckpt_flags = 0,
cp_pack_total_block_count = 5,
cp_pack_start_sum = 1,
valid_node_count = 1,
valid_inode_count = 1,
next_free_nid = 4,
sit_ver_bitmap_bytesize = 64,
nat_ver_bitmap_bytesize = 128,
checksum_offset = 4092,
elapsed_time = 0,
alloc_type = '\000' <repeats 15 times>,
sit_nat_version_bitmap = ""
}
7.4. Thuật toán tư duy
Từ quy trình trước đó và việc ghi lại summary block không đủ để hiểu toàn bộ check point, vì đây chỉ là quá trình khởi tạo. Nhưng có thể thấy rằng checkpoint tồn tại bản sao, và trải rộng trên 2 section, mỗi section có 2 bản sao check point.
Một tư duy thuật toán cơ bản là nếu lần trước ghi vào check point#1, thì lần sau sẽ ghi vào check point#0, điều này sẽ giúp kiểm tra tính nhất quán. Ngoài ra, quá trình recovery có vẻ cũng không bí ẩn gì, mặc dù hiện tại chưa thể biết thuật toán hoàn chỉnh, nhưng những gì làm ở đây chỉ là ghi lại metadata cần thiết, chỉ vậy thôi.
8. Kết thúc
Hiện tại đã hiểu đại khái về khung nhìn khởi tạo của F2FS, bài viết tiếp theo sẽ khám phá runtime của F2FS, tạm dừng ở đây.